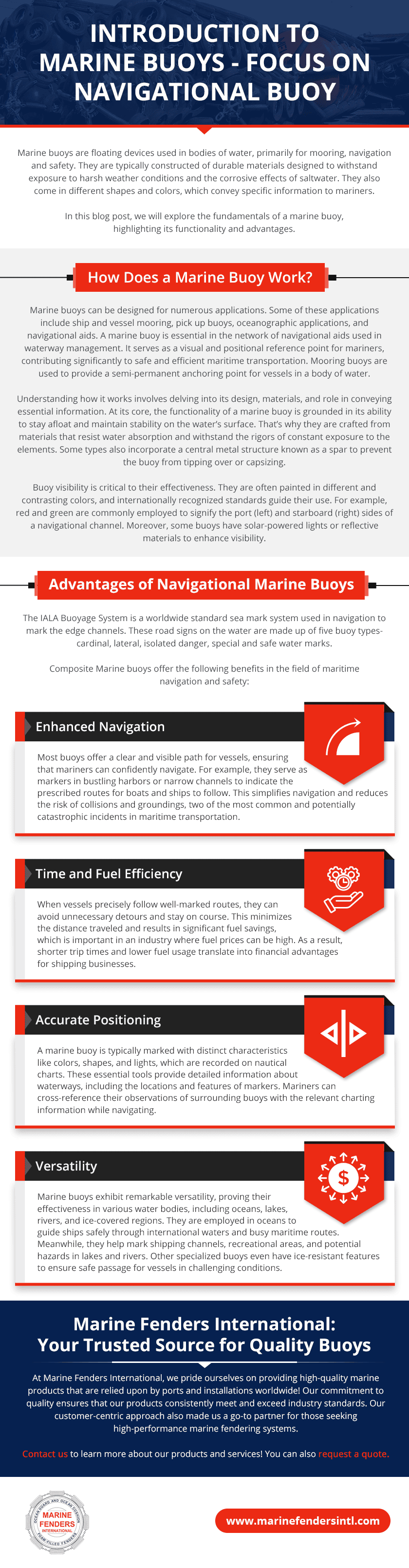
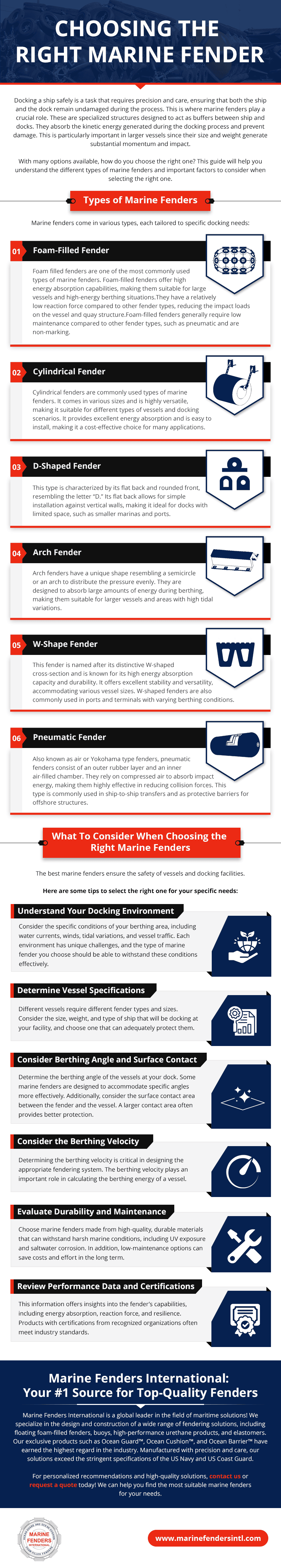
How To Choose the Best Ship Fender
Leave a CommentShip fenders act as protective buffers between ships, vessels and docks during mooring. They are typically made from durable rubbers or plastics; these cylindrical or spherical accessories absorb impact to prevent scratches and dents. They are designed to efficiently absorb significant amounts of energy with a low corresponding reaction force. By keeping these forces to a minimum significant structural cost can be reduced when designing a new or upgrading to a berthing facility. Fenders are attached to the hull or installed as floating or fixed on a quay wall.
Foam-Filled Marine Fender is a unique and innovative fendering system, providing high-energy absorption with a relatively low reaction force. Its heat laminated foam core allows it to reliably and safely absorb large amounts of energy when it is compressed. The closed cell aspect of the energy absorbing foam allows the fender to be fully functional even if the skin has been accidentally punctured.
Choosing a high-quality fender provides effective protection for the vessel and dock, mitigating the risk of costly repairs. It also provides safe berthing, reducing the risk of damage to vessel and or the dock. Here are several considerations when selecting the right boat fenders for specific maritime applications.
Factors To Consider When Selecting Boat Fenders
The following are some of the most significant factors to consider before purchasing a fender to ensure optimal performance:
Ship Size and Weight
Larger and heavier ships exert more force when they come into contact with a dock or other vessels. This force results from the ship’s substantial mass and momentum, especially in adverse weather conditions. The type of vessel also plays a critical role in choosing the appropriate fender. The vessel’s berthing velocity also is a critical component of the berthing energy and fender size required. Therefore, choosing fenders that can handle the impact is essential.
Undersized fenders may compress too much under the ship’s weight, potentially allowing the hull to come into direct contact with the dock. This can result in scratches, dents, or more severe damage to the dock or ship’s exterior. In contrast, adequately sized fendering systems will effectively take in the forces, safeguarding the vessel during docking and mooring.
Docking Conditions
The berthing approach,conditions, speed and angle are critical factor in determaining the appropriate fender size. Ships which frequently dock in areas with sharp or protruding hardware, must take those factors into account when choosing a fender type. The appropriate fender will provide superior protection and durability, making them ideal for scenarios where the risk of contact with abrasive surfaces is high. In addition, these fenders are constructed with reinforced materials and enhanced design features. Fenders can be designed for specific or custom applications.
Fender Material
The choice of fender material is critical and should align with specific ship, dock, and berthing needs. Here are some of the most popular options:
- Rubber: Durable and available in a variety of profiles. Typically has a higher reaction force to energy absorbed ratio.Cylindrical or conical shape
- Made of rubber or elastomeric material
- Absorb energy through compression and deflection
- Common types: Solid rubber, Pneumatic rubber, Foam-filled rubber
- Timber Fenders:
- Constructed from wooden beams or logs
- Absorb energy through compression and friction
- Often used in combination with rubber fenders
- Foam-Filled Fenders:
- Cylindrical or rectangular shape
- Filled with foam material (e.g., polyurethane, polyethylene)
- Absorb energy through compression and shear deformation of the foam
- High energy absorbing and low reaction force attributes.
- Capacity of the fender can be adjusted by the density of the foam core materials
- Pneumatic Fenders:
- Inflatable fenders filled with air or gas
- Absorb energy through compression and deflection
- Can be adjusted to different pressure levels
- Steel Fenders:
- Made of steel plates or tubes
- Absorb energy through elastic deformation
- Common types: Buckling pipe, Cylindrical steel
- Composite Fenders:
- Combination of different materials (e.g., rubber and steel)
- Designed to provide improved energy absorption and performance
- Donut Fenders:
- Designed to slip over a stationary monopile
- Float with the fluctuating tides
- Can be equipped with a mooring crown
- Provides all-tide mooring
Fender Attachment
The choice of fender will determine the attachments to be used for the overall safety and protection of the fender and ship . For example, chains are a traditional and reliable means of securing fenders. They involve securing the fenders to a dock plate or padeye. Other fenders may be bolted to a dock face while in certain applications floating fenders could also be secured by a chain to a dock or by a rope to a vessel.
Quantity
Using multiple fenders on each side of the boat is common practice. This arrangement ensures that the vessel is protected uniformly, reducing the potential for the hull to come into contact with a hard surface. Even protection is especially essential in variable docking conditions and when encountering docks with irregular shapes. Typically a single fender is sized to safely absorb the berthing energy of a vessel.
Budget
Balancing quality and cost is key. High-quality ship and dock fenders may come with a higher initial price tag but often provide superior protection and durability. On the other hand, lower-quality accessories may be less expensive upfront but can result in increased maintenance or repair costs down the line. Thus, spending more on first-rate equipment can be a cost-effective choice over time.
Marine Fenders International: Your Trusted Partner for High-Quality Marine Accessories
Marine Fenders International is an industry leader specializing in designing and constructing various maritime solutions! At the core of our offerings are our exceptional floating foam-filled fenders, donut fenders, buoys, high-performance urethane products, and elastomers. Our dedication to excellence extends to compliance with the US Navy and US Coast Guard standards Ocean Guard is Marine Fenders International trademarked brand name.
Contact us now or request a quote to get started!